GDPR – The General Data Protection Regulation is now effective from May 2018 which has been underway since 2012.
So, if you possess or work for an organization/individual who is in the European Union, then you should know the rules and regulations about the new EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Before going ahead to the GDPR Principals, let’s check
Jump to Section
What Is GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation is a new European Union (EU) regulation for Data protection. The main focus of this law is the following:
Improving and monitoring personal data operations nowadays.
The Regulation is effective from 25th of May 2018, and it will replace the current European Data Protection Directive.
This regulation of the EU will have extensive consequences for how organizations/individuals obtain, store, and use personal data, and they come into full effect this May 2018. It is expected to completely change the way of operating data.
Here, confusion on the term – “Personal Data” is becoming evident. Let me share my views with you on the topic.
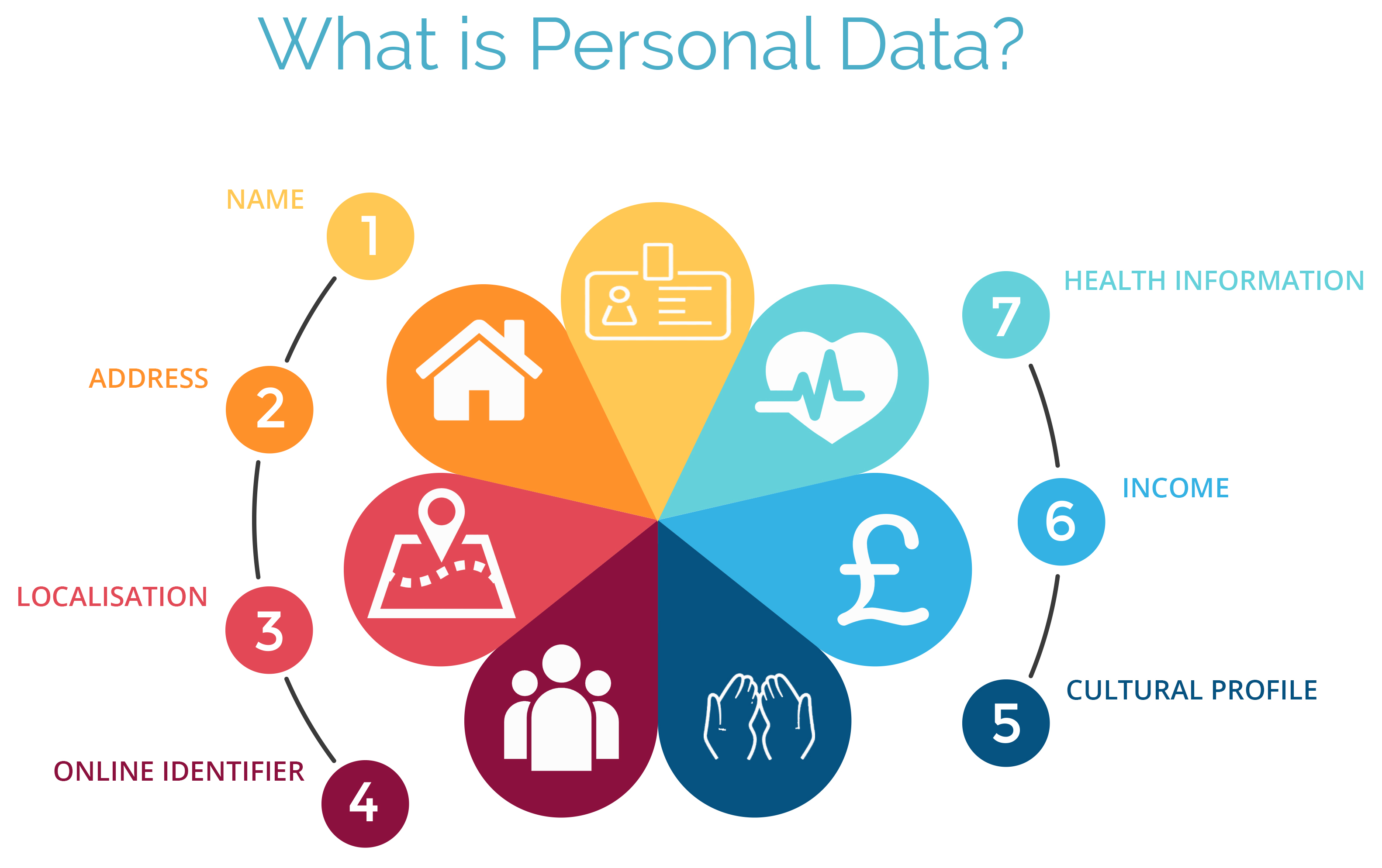
What Is Personal Data?
The idea of ‘Personal data’ is very widely explained. In general, it is usually a mode of information that connects to an individual’s secure data, like ID numbers, IP addresses, any physical or mental information, etc.
Personal data nowadays covers a broad range of information counting photos, bank details, social media names and posts, medical information, and many more. Therefore, any information which any users wish to keep secret information/data is Personal Data.
Who Does GDPR apply to?
To all organization that regulates, stores, or communicates any EU resident’s personal data, they need to follow the GDPR. This is mandatory for all data controllers and data processors.
What are Data Processors and Data Controllers?
Both complement each other. The controller operates how personal data is processed, and the processor helps for the same but both have an impact under GDPR.
The GDPR is by the European Union. Finally, it is not only for EU-based companies but also relates to organizations that are outside of the EU but provide services to their citizens or organizations. Any organization that breaches the regulation will find its annual global turnover or up to €20 million in fines. That’s too high to pay.
Also, regular breaches and operations will lead to higher fines of up to €40 million.
The National Data protection authorities in all jurisdictions will enforce GDPR. These authorities can privately sue any organization that is guilty of leaking personal data. Finally, the organization with a larger employee size can appoint a Data Protection Officer who will closely monitor all Data activities.
What Business Are Covered by the GDPR?
All areas of a business that acquires personal data, for example, HR, IT, sales, marketing, customer services, banking, finance, or legal including private and public sectors are covered by the GDPR. Therefore, personal data under GDPR also needs to be properly managed by all organizations.
Under GDPR regulation, all organizations all bound to provide every EU individual with a clear and transparent set of information about their personal data and its operations as follows-
- The right to be informed,
- A right of access,
- Rectification right,
- The right to erasure,
- Restrict processing right,
- Data portability right,
- The right to object,
- Rights in relation to automated decision making and profiling.
Now, we know all facts of The General Protection Regulation, let me put more light ahead on things to know about GDPR
10 things you should know about GDPR
1. For all organizations serving in the EU
Most of the companies or vendors who are serving in the EU might think that personal data comes under the GDPR category and might not think that GDPR will not impact them. Irrespective of any location, you are bound to follow this regulation act.
You must be GDPR complaint to serve your goods and services to the European Union (EU).
2. Specific GDPR Regulation for Controller and Processors
A controller is a person, public authority, or any company that decides to process the Personal data of EU citizens and has to strictly follow GDPR compliances.
A processor helps in the processing of that personal data on the count of the controller. There will be legal obligations for a processor to have all records of personal data in order to improve security.
3. Appointing a Data Protection Officer
A person who will monitor all activities of Data processing keeping GDPR in mind. DPO will follow the necessary protocols and helps the vendor to easily and comfortably work within the EU.
4. “Personal Data” views will change
Anyone will think personal data is something like Income information, ID number, bank details, and similar. Therefore, this type of personal data should be protected and carefully handled.
But, in GDPR personal data covers any information which is social, cultural, genetic, economic, and more, and will be covered under this regulation.
5. GDPR Compliance regulation date
The GDPR is effective from this May 25, 2018, so, all organizations must check and get ready for a complete change in the industry of Data processing.
6. Consequences for Non-Compliance
Those under compliance with GDPR and who have not followed the deadline will have to put in the fine which may be even higher than we can think.
These fines will vary, depending on the kind of breach, and will be charged accordingly. With this, we need to make sure to only use GDPR complaint means of communication for handling and processing data.
7. Personal Data collection must be clear
We need to make every operation of Data collection transparent to individuals that we are collecting their personal data and there needs to be clear information provided for the same. Ensure all GDPR complaints about personal data are handled accordingly.
8. Within 72-hour reporting of Data Breach
If there is a Data Breach of any privacy and comes under GDPR compliance, then it must be reported under 72 hours from the time of breach detection. If there is a delay in addressing, then again there is a fine separately for it.
9. Risks to victims
The organizations should immediately contact the concerned individual whose data is leaked or breached. Under GDPR, it’s not appropriate or “enough” to release the news of a breach via any social media or other means.
10. GDPR Compliance rules are different
The regulations under GDPR are different for each category of organization and compliance will vary accordingly. You can follow the GDPR checklist and get more details.
Steps as a vendor to comply with GDPR
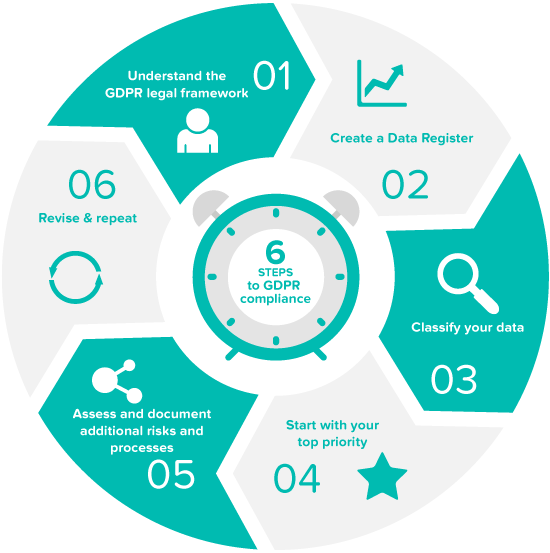
To prepare for GDPR, vendor organizations can use these step process:
1. Understand the law
Checking every GDPR notes of collecting, processing, and storing data, with all legislation special category.
2. Create a roadmap
Always create a plan for everything you do and keep them documented.
3. Classify Your Data
Checking if Data is coming under GDPR, if yes, then take effective measures for the same.
4. Start with the Top Priority
Risk assessment for all Data is necessary and applying security measures to data containing core assets.
5. Begin with critical data and procedures
Always check which Data processing needs more attention and care.
6. Revise and repeat
Repeat these steps and adjust findings where necessary.
Conclusion
Here is the conclusion part of the whole thing. Consider any personal data you acquire the same way you expect your personal data to be treated.
If you’ve already started thinking about GDPR and have good practices in place, it will surely be a good effort, but necessary actions must be in place. Despite the fact that it might seem hard at first, GDPR is the right step in the direction of data protection and should be welcomed.
- Business Intelligence Vs Data Analytics: What’s the Difference? - December 10, 2020
- Effective Ways Data Analytics Helps Improve Business Growth - July 28, 2020
- How the Automotive Industry is Benefitting From Web Scraping - July 23, 2020