Hola Tech Geeks!
Welcome to the world of Technology, where everything is the latest, user-friendly, and much simpler. Here, things may not be free of cost, but they would obviously be ‘free of bugs’.
Yes, you read it right. We all are in the era of Technology where technologies apart from being user-friendly, have to be bug-free as well! Now, you must be wondering bugs are the minor things that keep occurring after the development’s launch. But, it should not happen this way.
So, for making a Bug free development, we all first have to test that technology. Only then should it be introduced in between us. This is where the role of Software Testing comes in!
Jump to Section
What Is Software Testing?
Software Testing is the process of operating or checking a system or components of a system by checking it manually or by using any automation tools like selenium, HPE Unified Functional Testing (HP – U.F.T. formerly QTP). It means to verify that it satisfies specified requirements given by clients.
Source: www.midaswebtech.com
The Purpose and Objective of Software Testing:
Before taking further steps, let’s gain knowledge about the WHY and HOW of Software Testing…
Purpose of Software Testing:
Before testing any application or software or technology, we need to understand the purpose of testing it. The main purpose of software testing is to ensure that the developed application or software should meet the specified requirements provided by the Clients.
It also checks whether the complete software packages or applications are as per the client’s expectations or not.
The Objective of Software Testing:

Now, as we are aware of the purpose of testing, we can now proceed to the next step of understanding the Objective behind the Software Testing scenario. The whole process of Software Testing is loaded with many goals and objectives. The main objectives of software testing are as follows:
1. Helps in preventing defects.
2. It helps to make sure that the end result meets the business and user requirements.
3. Plays a pivotal role in finding the defects created while developing the application.
4. It helps in ensuring that the developed application or software, satisfies the BRS which stands for Business
Requirement Specification and SRS which stands for System Requirement Specifications.
5. Also, it helps in gaining confidence by providing a good quality product to clients.
6. It helps in providing information about the level of quality and also gaining confidence.
Quality Required in Software Development:
Before developing any software or application, we need to focus on the Quality of that software or application. The standard of quality must be high that further paves a green signal to its smooth development.
1. The software Testing and Test Designs are parts of quality assurance. It also focuses on bug prevention. A prevented bug is better than a detected and corrected bug.
2. For software, the quality of that software and productivity are indistinguishable. It is because the cost of a software copy is trivial.
3. The cost of bugs is the major part of software cost, it includes the cost of detecting them, correcting them, designing tests that discover them, and running those tests.
4. The Testing and Quality assurance costs for ‘DEVELOPED’ items can be as low as 2% in consumer products or as high as 80% in products like aircraft, space-ships, nuclear reactors, etc., where failures threaten life. Whereas, the manufacturing cost of software is trivial.
5. Trade-off between quality assurance costs and manufacturing costs: If the proper time is not spent in quality assurance, then the reject rate will be high and that will be the net cost and; if the inspection is good and all errors are caught at the same time when they occur, inspection costs will be dominant, and again the net cost will suffer.
6. In the production of consumer goods and other products, every manufacturing stage is subjected to quality control and testing from the component to the final stage.
7. The product is either discarded or cycled back for rework and correction if flaws are discovered at any stage.
Test Design:
The software code must be designed and tested in the earlier phase, but many appear to be unaware that tests themselves must be designed and tested. Tests should be properly designed and tested before applying them to the actual code.
Testing isn’t everything
There are approaches other than testing to create better software. Methods other than testing include:
1. Inspection Methods: Methods like walkthroughs, desk checking, formal inspections, and code reading appear to be as effective as testing but the bugs caught don’t completely overlap.
2. Design Style: While designing the software itself, adopting stylistic objectives such as testability, openness and clarity can do much to prevent bugs.
3. Static Analysis Methods: Includes a formal analysis of source code during compilation. In earlier days, it is a routine job of the programmer to do that. Now, the compilers have taken over that job.
4. Languages: The source language can help reduce certain kinds of bugs. Programmers find new bugs while using new languages.
5. Development Methodologies and Development Environment: The development process and the environment in which that methodology is embedded can prevent many kinds of bugs.
Types of BUGS:

Software is developed in some coding language and those codes are written by human beings. So, there might be some possibilities of having a mistake in it. Those mistakes are known as Bug, Defect, or Error. A software bug is an error, flaw, failure, or fault in a computer program or system that causes it to produce an incorrect or unexpected result. Or, it behaves in unintended ways. The process of fixing bugs is termed “debugging“.
Classification of Software Bugs
The Bugs can be classified into the following categories:
(1) Requirements, Features, and Functionality Bugs,
(2) Structural Bugs,
(3) Data Bugs,
(4) Coding Bugs,
(5) Interface, Integration, and System Bugs,
(6) Test and Test Design Bugs.
Software Testing Levels:
As we all know that the technology around has been created by someone. So, for creating technology, we need some steps. Software Testing Levels are basically to identify the missing areas and prevent overlap and repetition between the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) phases.
Requirement Gathering and Analysis, Design, Coding or Implementation, Testing, and Deployment have defined phases in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) models.
And each phase goes through testing.
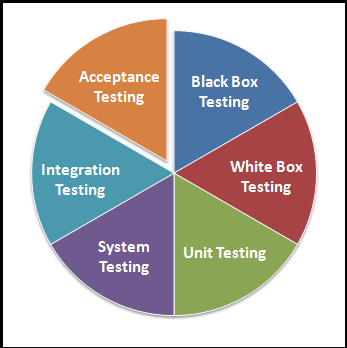
There are various levels of testing which are as following:
- Unit Testing
- Component Testing
- Integration Testing
- Component Integration Testing
- System Integration Testing
- System Testing
- Acceptance Testing
- Alpha Testing
- Beta Testing
Unit Testing:
Unit testing is a level of software testing in which individual components are tested. Unit testing is done during the development of applications or software.
The goal of unit testing is to isolate each part of the program and show that the individual parts are correct and to validate that each unit of the software performs as designed. Developers do the Unit Testing as during development they know the coding part.
Component Testing:
Component testing is the method where testing of each component in an application is done separately. Testers do the Component Testing. It is also known as module and program testing.
Component Testing is a technique of testing the lowest or the smallest unit of any application.
Integration Testing:
Integration testing is a level of software testing in which individual units are combined and tested as a group. It is mainly done when component testing is done and passed by Testing Team.
Suppose, you are doing Integration Testing. This would mean that you have to test two or more than two modules, so if in that module, a single component is not tested by the Testing team, it will be a waste of time and cost to do integration testing at that time. Before testing, all the components should be as per the users’ requirements. Below are a few types of integration testing:
- Big bang integration testing,
- Top-down,
- Bottom-up,
- Functional incremental.
Component Integration Testing:
When two modules or components are integrated, then the testing of both modules is called Component integration testing. This testing is done to ensure that the code should not break after integrating two modules simultaneously.
System Integration Testing:
When all the modules or components in any system are integrated, then the testing of all modules is called System integration testing. This testing is done to ensure that the code should not break after integrating all the modules.
System Testing:
System testing is defined as the testing whole system, or you can say, testing a system from starting to end after integrating all the modules or components. It is done just before the Acceptance Testing level.
Acceptance Testing:
Acceptance testing is basically done after System testing is completed. It ensures that the requirements of the specification are met. It is of two types, one is Alpha Testing and another is Beta Testing.
Alpha Testing is done by in-house developers at their own place. On the other hand, Beta testing is done by selected users who will use or operate the application in an end-user role and they will provide feedback if present.
Software Testing Types:
Before starting our testing process, first, we need to understand the types of Software Testing. Software Test types are known as a means of clearly defining the objective of a certain level for a program or project.
A particular test objective is being focused on a Software Test type.
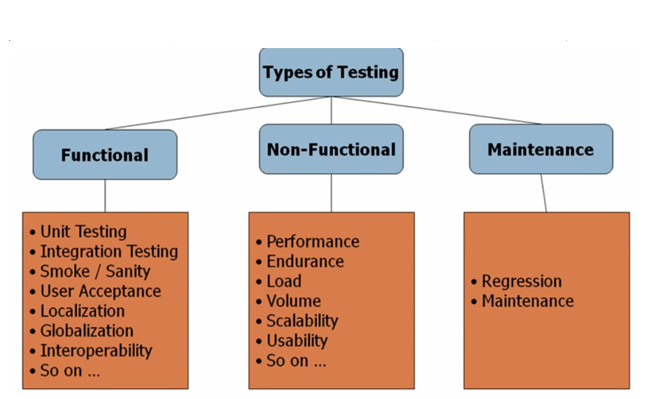
The Software Test Types can be classified into the following categories:
- Functional testing,
- Non-functional testing,
- Structural testing,
- Change-related testing.
Functional Testing
Functional Testing is a quality assurance (QA) process. It is a type of Black Box testing that bases its test cases on the specifications of the Software component under test.
It involves entering Input and examine the Output for testing the functions. Functional testing usually describes “WHAT THE SYSTEM DOES“.
Functional testing includes:
- Smoke testing,
- Sanity testing,
- Regression testing,
- Usability testing.
Non-Functional Testing
Non-function testing is the testing of a Software Application for its non-functional requirements such as Security Testing, Load Testing, Volume Testing, etc.
Non-functional testing includes:
- Reliability testing,
- Usability testing,
- Efficiency testing,
- Maintainability testing,
- Portability testing,
- Baseline testing,
- Compliance testing,
- Documentation testing,
- Endurance testing,
- Load testing,
- Performance testing,
- Compatibility testing,
- Security testing,
- Scalability testing,
- Volume testing,
- Stress testing,
- Recovery testing,
- Internationalization testing and Localization testing.
Structural Testing
Another type of testing is Structural testing. It is the type of testing carried out to test the structure of the code. It is also known as White Box testing or Glass Box testing. The developers have done the structural testing, they have the knowledge of code. It is more concerned with how the system does it rather than the functionality of the system.
Conclusion
Now we can conclude as Software testing is an important part of the software development process. A successful test strategy will begin from the requirements specification.
As with the other activities in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), Testing has its own unique challenges. As software systems become more and more complex, the need for Testing increases with more well-planned testing efforts.
Software testing is very important because Testing makes sure of the Customer’s reliability and satisfaction in the application. Since, we assume that our work may have mistakes, hence we all need to check our own work. Testing is important as it uncovers a defect, before delivering the product or application.
- COVID-19: How We Are Dealing With It as a Company - March 23, 2020
- Agile Testing – The Only Way to Develop Quality Software - February 8, 2019
- How to Perform System Testing Using Various Types Techniques - May 16, 2018



Nice Blog and you have explain each & every thing clearly:)
Thank yo so much Bharat…
Nice blog