System Testing is the stage in testing line, to evaluate the system as a whole called software build, but not on its parts. After the completion of unit testing and Integrated testing phases, we place System Testing. The goal of System testing techniques is to evaluate the system as a whole and imitate customer deployments. This testing stage evaluates the system standards with its specified requirement and quality factors. System testing helps in uncovering the defect that may not be directly attributable to a module or an interface in between modules. System test planning consists of the creation of the environment required for testing the product. This environment is close to the user environment consisting of hardware, software, communications, and any other support tools. The independent QA Engineers(s)/Test Engineers carry out system testing on the software product.
Jump to Section
Roles and Responsibilities
Roles which involves their corresponding activities are as follows:
-
Individual/Group Activities Testing/QA Group Execution of System Test Cases Development Team Members Fix Defect/Bugs
Input
The input documents to be provided to carry out the system testing process are:
- System test planning
- System test cases
- Software project plan
- Software Measurements/ metrics plan
- SQA plan
Tasks
Here we listed out the tasks usually during this process. The System testing team may be doing these activities almost in the same sequential order:
- First of all, we need to Set up system testing environment
- Perform system testing using baselined system requirements allocated to the software, baselined functional requirements specifications documents, and baselined software source code as Build.
- Executes all system test cases.
- Document and track problems identified during system and acceptance testing to closure.
- Review and close reported defects, use bug tracking tool to track the defects/bugs.
- Determine if software source code satisfies system requirements allocated to software and functional requirements specifications documents, based on system testing results.
- Update the project data collection sheet.
Output
Finally, this is the Output. So, the documents which produce the output from system testing, contains different phases are as follows:
- System testing defect/bug summary reports
- Updated project data collection sheet.
Exit Criteria
The completion of system testing process also contains two criteria:
- System testing conducted and all the defects closed
- Baselined the system tested the software product.
Measurements and Metrics
System Testing Team usually follows two metrics to ensure these works:
- System test Defects
- Review and rework effort
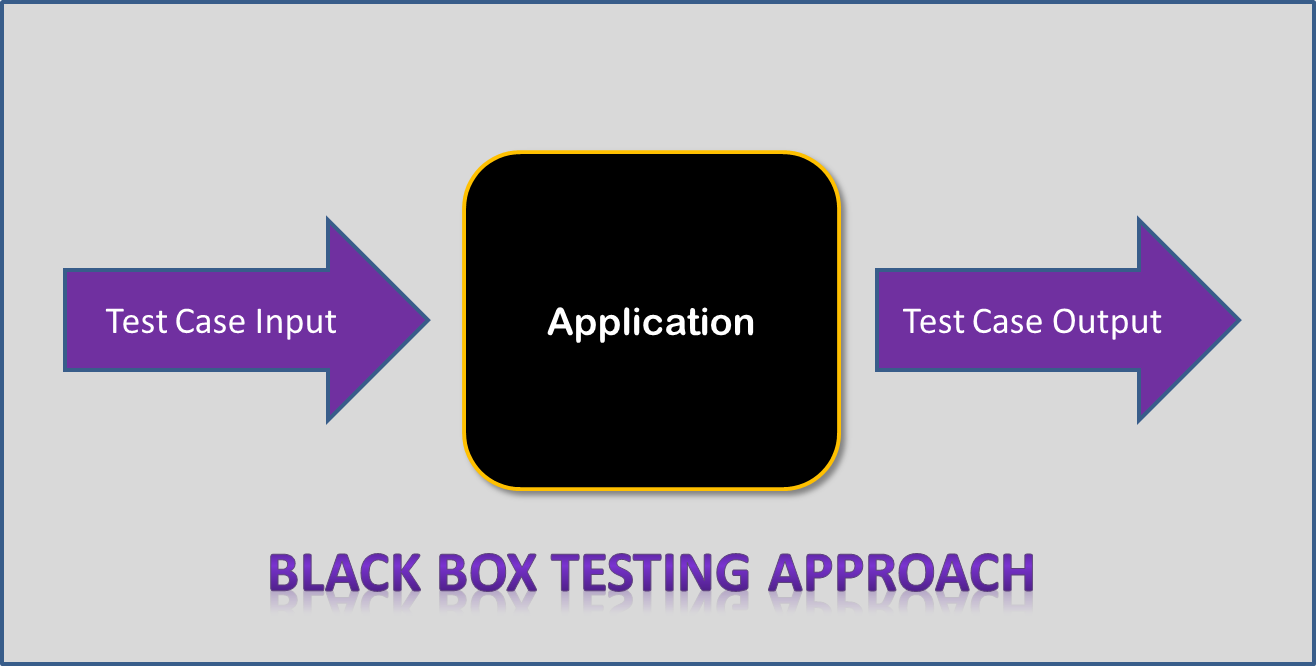
Black Box Testing
Definition-based or specification-based testing is also known as Black box Testing. So, it identifies the test cases based on the definition of what the software product is intended to do. Therefore these test cases challenge the use or functionality of a program and the program’s internal and external interfaces. We can apply Black box Testing at System level of software testing. So, the following types of Black Box Testing generally involve the following increasing level of effort:
Normal Case- This is a technique usually based on necessary inputs and just concentrates on the basic functionality of software build.
Robustness- Software testing should demonstrate that a software product behaves correctly as a result when given unexpected, invalid inputs.
Combinations of inputs- The Black Box testing methods identified above, stress on single test inputs. Most software products operate with multiple inputs under their conditions of use.
The first three methods are for identifying a sufficient set of such test cases including Equivalence Class Partitioning, Boundary Value Analysis, and Special case Identification like Error Guessing. These techniques do not ensure all of the most appropriable challenges to a software product. We can extend Error guessing to identify communications of inputs, but it is an Ad-Hoc Technique. Cause-effect graphing is one of the black box testing techniques that systematically identifies combinations of inputs to a software product for the inclusion of test cases.
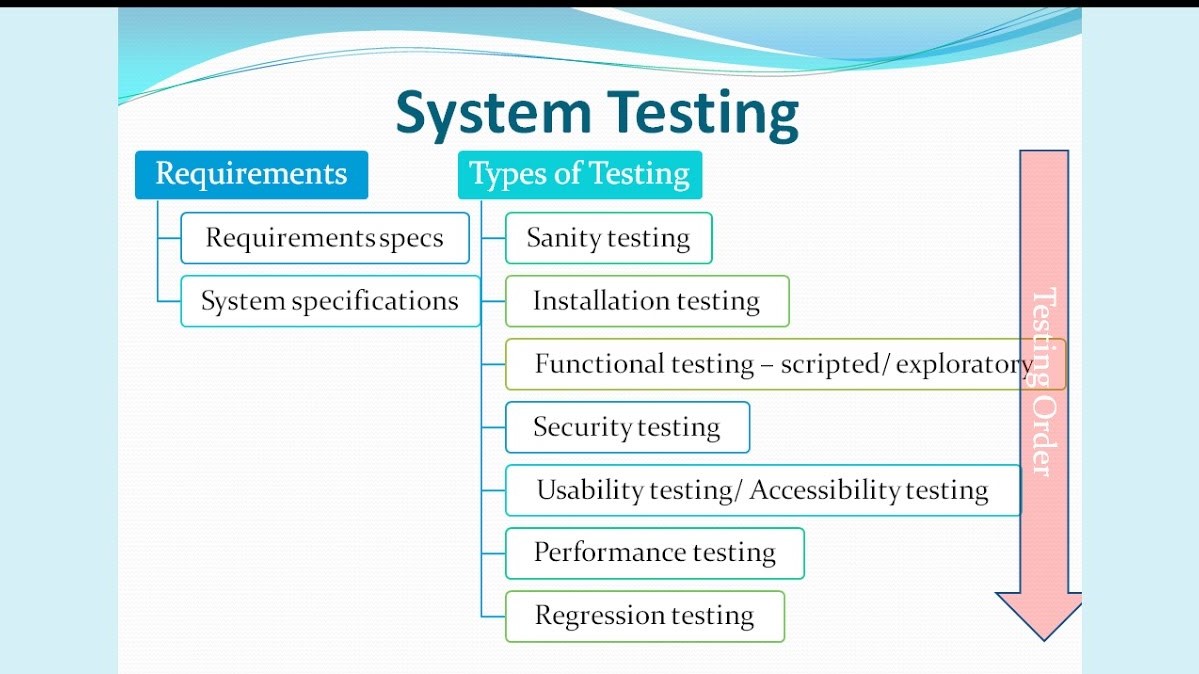
SYSTEM TESTING TECHNIQUES
System Testing is the only phase of testing, which tests the usability, functional and other non-functional aspects of the product. It starts when the unit and integration testing are complete, which ensures that the more basic program logic errors and defects which in the correct format. Including the validation of the business requirements of the product. It is done to make sure that the product is ready for moving to the user acceptance test level.
The non-functional aspects of the product, such as performance, security, compatibility, and installation can require considerable effort to test and perfect. These testing techniques, like Usability, functional and non-functional testing are acted upon the source of written test cases according to the information collected from high-level design documents, detailed design documents, and software requirements specifications.
Usability Testing
Usability is a combination of factors that influence user experience with a product of a system. It is a methodical evaluation of the graphical user interface to measure the quality of a user’s experience when interacting with a system. This testing carried out the experiments to find out the specific information about a user interface design.
This testing is used throughout the software development lifecycle. In early stages of software development, testing the previous version or competitor’s product, give the user interface design team benchmarks to efficiently, effectively and satisfactorily design the user interface of that software product. If we talk about the middle stages of development, Testing validates the user interface design and provides with feedback that refines the design of user interface. In the later stages, like system testing, the usability testing ensures that the software product meets the user interface design objectives through a few subsets that include:
User Interface Testing
In user interface testing, we have to test three factors on every screen of the build:
- Ease Of User
- Look And Feel
- Speed In Interface
Manual Support Testing
During this test, Engineers check context sensitiveness of the help documents. It is also called help documents testing. System test cases can also be developed based on a customer discussion and the usage level of end-user on the customer site.
Functional Testing
After completing the user interface testing, test engineers concentrate on functional testing to validate customer requirements. It involves testing product functionality and features. This testing helps in validating what the system suppose to do. It has only two results as far as requirements fulfillment is concerned-met or not met.
Basically, It defines simple methods and steps to execute the test cases and those test cases result normally depend on the product features, and not on the environment. It requires in-depth customer and product knowledge as well as domain knowledge to develop different test cases and find critical defects. A defect in functional testing normally indicates changes in the code to arrive at the right behavior. So if the listing of requirements is not properly, we can understand the functional requirements through the operation of the product in terms of the behavior of that product.
Generally, Functionality checking performs in all phases, such as unit testing, integration testing, and system testing, but the functional testing is done if the system testing phase focuses on product features in the earlier phase of testing.
The types of techniques used in performing functional testing include:
- Behavioral Coverage/ GUI Coverage
- Error Handling Coverage
- Input Domain Coverage
- Manipulations Coverage
- Backend Coverage
GUI Coverage
In this coverage, test engineers finally observe the behavior of objects in screens of product with respect to the corresponding functionality and validate changes in properties values of objects, which are involving in the testing functionality of the product.
Error Handling Coverage
In this coverage, as a result, test engineers observe the behavior of objects with respect to invalid events. For Example, if a user operates object or control wrongly, then our product returns a meaningful error message to indicate a wrong event on that object.
Input Domain Coverage
Test Engineers go to special treatment to input domain testing in terms of Boundary Value Analysis(BVA) and Equivalence class Partitions(ECP). So BVA Concentrates on range or size of the input object. ECP concentrates on the type of the input objects.
Manipulations Coverage
In this coverage, test engineers validate output or outcome of that corresponding functionality at the end. For Example, a login operation in website returns inbox of that user at the end of login operation with valid input data.
Backend Coverage
In this Coverage, test engineers validate the impact of the front-end functionality on the backend database tables in terms of data validation and data integrity. Test engineers validate the place of testing functionality in that product, e.g. before login to a website the new user registration option occurs.
Non-Functional Testing
As you know that software community goes competitive day by day. Hence, its time for an organization to have a look at a few non-functional requirements, like performance, security, compatibility, and reliability, apart from the functional and usability aspects to deliver quality software. These non-functional requirements will associate with their corresponding functional requirements and will define during the requirements phase. If non-functional requirements do not define, the requirements as a whole should consider incomplete and probably will not receive the appropriable attention, until late in the development lifecycle.
Basically, It performs to verify that the develope system builds work properly with respect to the Non-Functional requirement, like performance, security, compatibility, and reliability. It attempts to determine that the technology has been used properly and that when all the components part assembles, they function as a complete system. The non-functional system testing techniques are briefly described.
Load Testing
The execution of our build under customer expectations and the load to estimate performance called LOAD TESTING. In other words, we can call it as Scalability Testing.
The objective of Load Testing or Scalability Testing is to find out the maximum capability of product parameters. As a result, the exercise involves finding the maximum resources that need. For this, kind of testing is normally very high. For example, one of the scalability test cases could be finding out how many client machines can simultaneously log in to the server to perform some operations. In Internet space, some of the services can get up to a million accesses to the server. Hence, a high-end Configuration can select and the scalability parameter increases step by step to reach the maximum capability.
Stress Testing
Basically, Test engineers perform Stress Testing for evaluating a system which beyond to the range of specified requirements, for ensuring that does the system break or not. The product is almost over-loaded deliberately to simulate the resources crunch and to find out its behavior. We expect to gracefully increase the load, but the system can not expect to crash during stress testing at any point.
Recovery Testing
While executing recovery testing we check that how well our machine or software recovers from the crashes, hardware failure, and catastrophic problems are known as Recovery Testing. In this testing, with the help of recovery procedures and backup, an application can go to abnormal to normal state.
Recovery is the ability to restart operations after the integrity of losing the application. The time requires to recover operations is affects by the numbers of restart points, and the tools available for recovery. Hence, the importance of recovery will vary from application to application.
Installation Testing
After completing the functional test, the testing team basically focuses on installation and uninstallation of the build at the customer site. Once the Installation team has completed its efforts. System testing takes that integrated product to validate the features and services. Basically, engineers design System testing for ensuring that the system requirements and specification are achieving or not at the time. This testing generally involves creating test conditions for the use of evaluating the correctness of the application.
Conclusion
In conclusion, The organization involved in software development of added complex products or less complex products need to analyze the various stages of the software development lifecycle very clearly. Finally, the main purpose of this article is to establish the possession clearly for System Testing. This will help to simplify the overall management of System Testing phase, including each identified stage needed to establish a well-defined end-to-end process of managing the testing activities.
- COVID-19: How We Are Dealing With It as a Company - March 23, 2020
- Agile Testing – The Only Way to Develop Quality Software - February 8, 2019
- How to Perform System Testing Using Various Types Techniques - May 16, 2018