There was a time when patient records were manual, and hospitals used traditional methods of managing hospital supplies and medicines. Doctors too relied upon diagnostic tests for diagnosis and patient treatment. However, with patient records being digitized, hospitals and doctors have a huge amount of health-related data at their disposal.
The IoT (Internet of Things) network of health tracking devices that generate a continuous stream of patient data is also being accessed by physicians for devising the best line of treatment. This has led to the generation of vast data within the healthcare system which is now being used to drive advantages for the healthcare sector.
Jump to Section
Healthcare data is powering an innovation trajectory
Legacy IT systems are being replaced by innovative technologies that leverage the ‘big data” for insights and data-driven decisions. Predictive analytics is being used more and more for enhanced healthcare deliveries and optimization of processes.
The demand for high-quality healthcare services is on the rise, together with granular personalization in healthcare services. Patients are being treated on par with customers in other industries, and hospitals and healthcare providers are using actionable insights for a better CX (customer experience) and faster ROI (Returns on Investment).
Trends driving the use of Big Data Analytics in Healthcare
- According to the report by Market Research Future, the global healthcare big data analytics market is expected to grow at a CAGR of about 11.5 %, to reach USD $9.5 billion in 2023, from USD $5.5 billion in 2016.
- Although historically, North America has witnessed the biggest implementation, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to be the fastest-growing market.
- Huge population coverage under healthcare spurred by increasing government spending, growing digitization, and advancement in big data technologies. These have contributed to the rising deployment of big data analytics in various areas of the healthcare industry across India and other Asian countries.
- Big data analytic solutions tap the zettabytes of healthcare data to improve the quality of patient services and improve the overall healthcare ecosystem in facilities and hospitals.
- With rising costs of healthcare spend, governments are spearheading efforts at healthcare reforms, prioritizing patient care and hospital facilities.
- Additionally, the data generated is being used for research into preventive healthcare and the development of health initiatives.
- Data from grocery store purchases, social media, pollution levels, and health insurance claims are also being integrated to better understand the impacts of food and the environment on individual and population health.
- As big data analytics finds adoption amongst healthcare providers, hospitals, and pharmaceutical companies, the trend can be expected to increase phenomenally over the next few years.
A look at how Big Data is generated
How is so much data generated within the healthcare industry? Which are the touchpoints of data creation and analysis? To what end does the analytics drive changes within the healthcare industry?
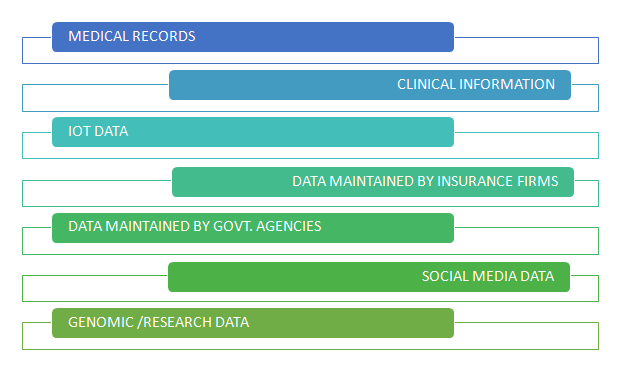
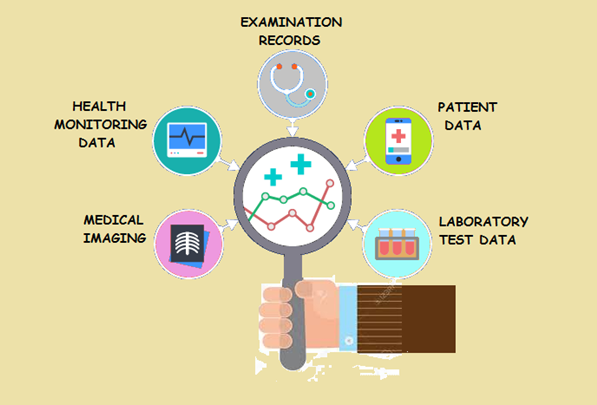
Here are some points of data creation that together contribute to the voluminous data in healthcare:
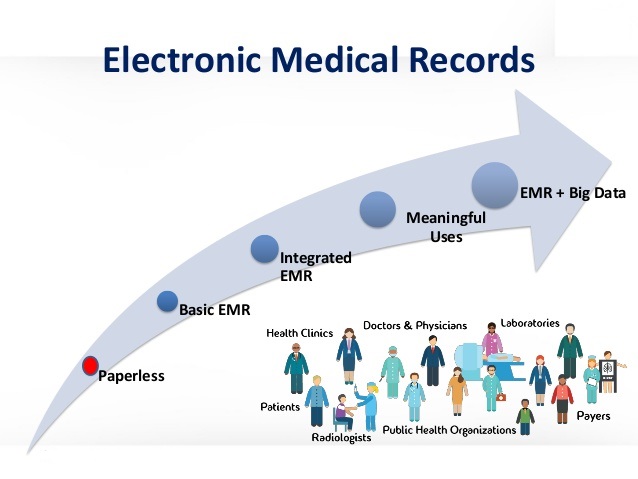
Electronic Medical Records
The clinical history of patient data maintained by doctors provides a comprehensive picture of a patient’s health record. This includes the physician’s notes, diagnosis, and treatment.
Other Clinical Information
Clinical data also include diagnostic and prescriptive records entered by doctors, patient profiles, and medical prescriptions. There is also plenty of administrative data related to the logistics and supply of medicines used within the hospital. Insurance claims data is another set of healthcare data that is finding popular use amongst insurance companies.
IoT data
The proliferation of wearable devices, online health monitoring apps, and connected medical devices have generated huge streams of data in the IoT network. Medical devices and sensors like pulse monitors and electronic weighing scales, as well as wearables that track heart rate, blood pressure, or activity levels send streaming data to the cloud. Healthcare apps on smartphones track a user’s exercise activity and quality of sleep. All of this data is stored in the private cloud for sharing and analysis by various stakeholders. This data can be accessed by:
- Insurance providers,
- Health care practitioners,
- Public health services,
- Medical and pharmaceutical manufacturers, and
- World health organizations that function as community health watchdogs.
Data Maintained by Insurance providers and Government Health Agencies
Medical Insurance covers healthcare, accidents, and specific diseases. This gives rise to huge data related to policy coverage types, claims, and government health plans.
Social Feeds
Healthcare providers are much dependent upon brand image for patient loyalty and competitive edge in a crowded, competitive marketplace. So unstructured data generated from social media conversations and forums are another source of data, analyzed for improving patient care and customer services.
Opt-In Genome and Research Registries
Many genomic research organizations gather volunteered patient data to support research in clinical trials and preventive healthcare.
Together, these touchpoints of data creation contribute to gigabytes of structured and unstructured data within the healthcare industry.
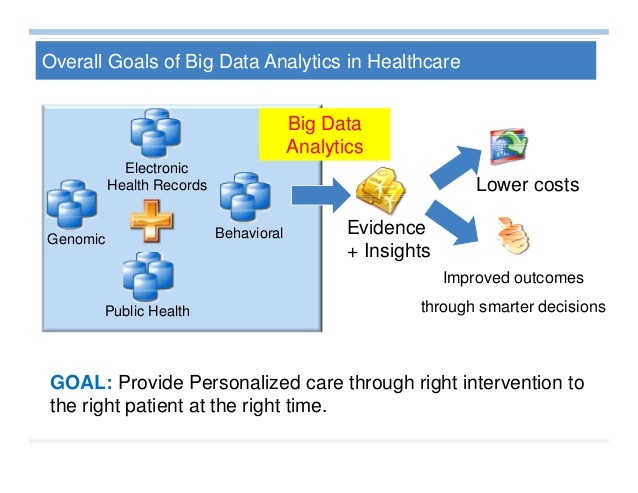
How Big Data Analytics Brings Value in Healthcare
Big data analytics offers various benefits of data-driven insights to individual healthcare practices as well as large facilities or Government health departments. At the micro-level, predictive analytics and models help to offer better patient care and optimization of resources. At the macro level, healthcare data collected across agencies, regions, and ethnicities over a span of time can help develop a comprehensive picture of global health conditions for data-driven policymaking.
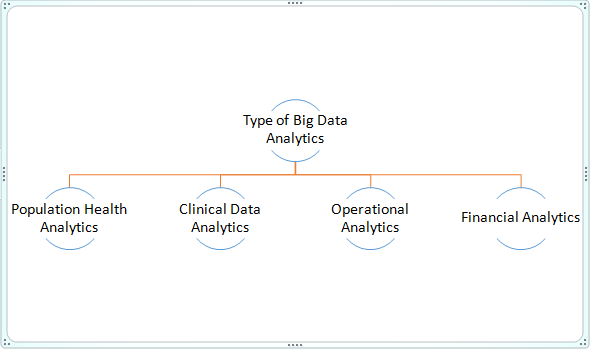
POPULATION HEALTH ANALYTICS IS USED FOR
Below are the most common uses of population-based health analytics.
Public health management
- Analytics of data related to diseases, patterns of incidence, and outbreaks can help understand the cause of outbreaks and locations to predict and prevent future occurrences.
- Such public health data, when shared between participating agencies like the government and civic planners, can support the discovery of hidden patterns and linkages.
- For instance, data related to dengue outbreaks can not only help the civic authorities investigate the underlying cause in the location, but also facilitate suitable measures to control the spread.
- The spread of the Ebola disease could be contained only through analysis of data collected at local sites and healthcare facilities.
- This hasn’t only enabled the timely deployment of medicines, equipment, and health care providers to the locations, but also helped to develop models that could predict the sites of high-risk incidence before they even occur.
Policy-making by global health organizations
Data collected from individual health practitioners, facilities, hospitals, pharmaceutical and insurance companies, government health and municipal departments all help build world health databases. Analytics of the data help determine, for instance, demographies at high risks of malnutrition or disease and support appropriate policymaking and regulations.
CLINICAL DATA ANALYTICS IS USED FOR
Patient healthcare management
Patient data analytics is used to ensure quality control of healthcare, and ensure that the norms of diagnosis and treatment are adhered to. Advances in analytics applications can now even spot a patient not taking his medicine!
Improved services and preventive healthcare
Analytics of patient data across departments can help determine quick and cheap ways to diagnose and treat patients. Drug prescriptions and success rates are correlated to discover optimal treatments, drugs, and devices. Clinical trials are analyzed using big data analytics prior to the launch of a medical device or drug.
Patient Profiling
Predictive analytics models help identify patients who may benefit from measures like diet, lifestyle changes, and therapies. Analytics also helps identify whether patients affected by say, an auto-immune disease, have the risk of contracting other diseases like diabetes. In case of diseases related to specific ethnicities, analytics of affected patients can help better disease management.
Finding cures for diseases
Genome analytics is being used to develop insights into the human genomes to detect patterns for the detection of diseases like cancer. As no two persons have the same genetic sequences, response to the line of treatment also varies for persons. The study of genomic medicine creates huge data, which, when analyzed, can uncover unknown correlations and hidden patterns. Doctors are now finding value in these insights to engineer a correct treatment or drug suited to the individual level.
Pharmaceutical /Medical Equipment Companies to Meet Requirements of Patients and Hospitals
Patient records, drug prescriptions, disease incidence data, and lab tests help pharmaceutical companies to leverage predictive analytics for the production and supply of medicines and medical devices.
Actuarial Use
Hospitals partner with insurance providers to share patient data and hospital admission data. Predictive analytic models built on such data matched with actuarial tables help develop health plans and devise insurance premiums.
OPERATIONAL ANALYTICS IS USED FOR
- Fraud Management– Analysis of insurance claim requests can help identify cases of fraudulent claims. Similarly, insights into hospital processes can help identify fraud.
- Safety Monitoring– The large volumes of streaming data generated in hospitals, when analyzed, can help monitor safety measures and predict negative event occurrence.
- Optimizing facility performance– Analytics as a business intelligence (BI) strategy can be beneficial for operational efficiencies. For instance, analysis of hospital admission rates can help identify issues like poor emergency care or staff inadequacies.
Performance analytics of different points of operational silos and bottlenecks can aid in the reduction of wastage and inefficiencies. Resource use in areas like energy consumption, security services, and store supplies; can be better optimized with analytics.
The big data ecosystem allows equipment diagnostics and analytics in real-time for timely maintenance and prevention of system breakdowns. This ensures a seamless facility operation and enhanced patient service, with better patient safety, and facility brand ratings.
FINANCIAL ANALYTICS
Ultimately, healthcare practitioners, facilities, and government hospitals are financially accountable to shareholders or government audit reports. Analytics of the huge amount of financial data, can help facilitate claim processing, enable risk assessment, manage the revenue cycle and prevent financial crime.
Case Studies from India and the World
- Apollo Hospitals in India tackled the problem of ‘Hospital-Acquired Infection’ using an analytics model.
- Disease and infection data across clinical and non-clinical departments like microbiologists, laboratory teams, doctors, and pharmacologists were leveraged to discover preventive and prescriptive treatment methods to tackle in-house infections.
- The Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto captures and analyses medical monitor data in real-time to drive“near-real-time decision support and retrospective analysis” of treatment.
- Atlanta (U.S.) based Piedmont Healthcare deployed analytics tools to provide better outcomes for its Medicare patients with pneumonia.
- In less than one year, the readmission rate for patients with pneumonia was reduced by 26 percent.
Bottomline
The advantages of big data analytics in healthcare are many, with each stakeholder or partner able to use actionable insights for optimal healthcare solutions and services. The underlying value of the huge data created is thus considered a veritable goldmine, with each day finding new applications of healthcare data analytics.
- Business Intelligence Vs Data Analytics: What’s the Difference? - December 10, 2020
- Effective Ways Data Analytics Helps Improve Business Growth - July 28, 2020
- How the Automotive Industry is Benefitting From Web Scraping - July 23, 2020